The Chemistry Society at University of Toronto Scarborough (CSU) is an organization that collaborates with students to cultivate innovative and fun academic events focusing on fostering relationships between the faculty and the students


The Chemistry Society at University of Toronto Scarborough (CSU) is an organization that collaborates with students to cultivate innovative and fun academic events focusing on fostering relationships between the faculty and the students

We aim to provide the students of UTSC with the representation and resources they need for success.
We host events varying from social mixers between students and mixed student-faculty events, workshops for important chemistry techniques, office hours for chemistry lab help, field trips to bring chemistry in context and more.
Our mission is to cultivate a chemistry community on campus and push for the growth of Chemistry as a department at the University of Toronto Scarborough.
We provide .....
The Covalent Network Program is a program where CSU members can have benefits include:
The Chemistry Aid Centre is a centre co-ran by the Environmental and Physical Sciences Association (EPSA) and our organization. The centre provides in-person help to assist students in course material such as prelaboratory help, laboratory techniques and course content.
Below is the Chem-Aid Centre Schedule:
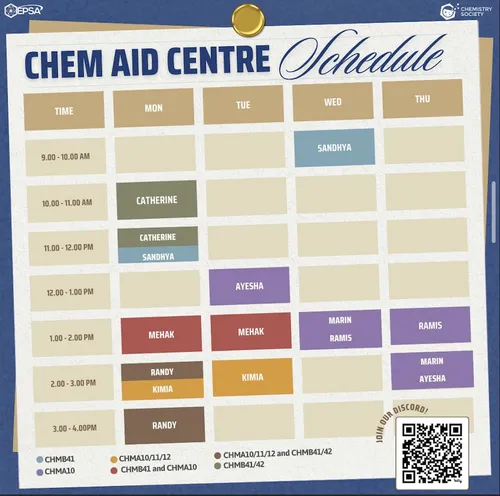
The Chemistry Society at UTSC provides time for our CSU members to talk to the executive team to chat about social and academic issues. Members are free to use our Chemistry textbook library, whiteboard to solve questions and eat from our office snack bar. Below is the schedule!

Co - President

Co - President

Vice President External

Vice President Internal

Outreach Coordinator

Outreach Coordinator

Director of Finance

Chem-Aid Director

Director of Academics

Director of Academics

Director of Marketing - Social Media

Director of Marketing - Graphic Design

Director of Marketing - Graphic Design

Director of Marketing - Graphic Design

Director of Marketing - Web Master

Director of Events

Director of Events

Director of Events

At UTSC, there are so many different options you have in the field of chemistry! Whether you're passionate about biological chemistry, physical chemistry, environmental chemistry, or just chemistry as a whole, there's a program for you.
You can choose from six different Major programs: Chemistry, Biochemistry or Environmental Chemistry (all with or without Co-op), as well as their Specialists equivalents: Chemistry, Medicinal and Biological Chemistry or Environmental Chemistry (all with or without Co-op).
Each program has their own faculty advisor to contact for any questions and/or advice, which can be found here along with more information about each POSt: POST Information

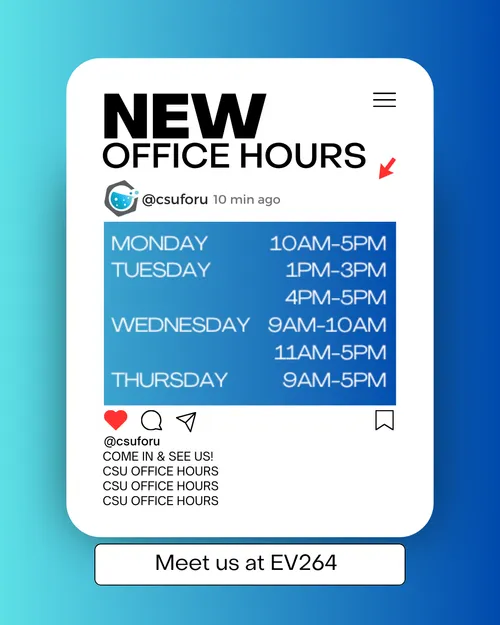
Chemistry courses can be tough. In order to provide free and strong academic support to students at UTSC, we run an incredible Chemistry-Aid Centre (with EPSA).
During scheduled office hours, students can drop by either virtually or in-person in our office, EV 264, and ask any and all questions to upper-year student tutors. This Centre is open every day of every week, all semester long (Week 3 or 4 of classes to Week 12).
Please use the following Discord invite link to join the Centre and boost your learning today! Server Link

The Chemistry Society at the University of Toronto Scarborough (CSU) is an organization that collaborates with students and faculty members to provide innovative and fun academic events focusing on providing networking experience and volunteer opportunities, increasing the passion for science and helping with their academic growth and mentorship.
Our mission is achieved by hosting events varying from social mixers between students and mixed student-faculty events, workshops for essential chemistry techniques, office hours for chemistry tutoring help, and more.
Our goal is to cultivate a chemistry community on campus and push the growth of Chemistry as a department at the University of Toronto Scarborough.

Future paths that would open the door with your chemistry degree can open various gateways to many career paths, offering opportunities across diverse industries.
Graduates can delve into research and development, applying their expertise to pharmaceuticals, materials science, or the chemical industry.
Besides industry, the academic route would open toward teaching and groundbreaking research.
Since the creation of the first robot in 1929, the applications of AI in academic and professional fields have significantly expanded. One of its most significant uses is in drug discovery. Developing new medications often takes over a decade and costs billions, but AI is making it faster and more cost-effective.
AI algorithms can analyze vast chemical datasets to identify patterns that suggest which compounds would be effective in targeting specific biological pathways. Machine learning models simulate compound behaviour, predicting their efficacy and safety based on historical data. This focus allows researchers to prioritize candidates with a higher chance of success in clinical trials. Moreover, AI automates the screening of thousands of compounds to assess their interactions with biological targets, streamlining the identification of promising drug candidates. It also aids in drug repurposing by assessing existing medications for new applications, discovering novel relationships between drugs and diseases, and facilitating faster therapeutic solutions.
Additionally, AI also enhances the design of clinical trials by identifying suitable patient populations and optimizing trial protocols, improving recruitment and overall execution. A prime example of AI's impact is Atomwise. It utilizes deep learning algorithms to find potential treatments for diseases like Ebola and multiple sclerosis.
Every decade has seen discoveries in medications for life-threatening diseases. However, many deaths today are caused due to unknown diseases, ones that still do not have medications. The future of drug discovery is promising due to AI's high processing power and information retainability, with a commitment to save millions of lives.
Feb 25, 2025
Artificial intelligence (AI) is reshaping the scientific landscape, accelerating discoveries, and offering innovative solutions across multiple fields. From drug development to climate science, AI is transforming the way researchers approach complex problems, making scientific advancements faster and more efficient.
One area where AI is making a profound impact is in medical research, particularly in the discovery of treatments for previously incurable diseases. A compelling example is the case of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF), a devastating lung disease that causes scarring of the lungs and progressively limits a person's ability to breathe. Traditionally, drug development for such conditions takes years and requires immense financial investment. However, AI is revolutionizing this process by drastically cutting down both time and costs. Insilico Medicine, a biotech startup, leveraged generative AI to design a new drug for IPF. Their AI-powered system identified potential treatment targets and created a drug candidate in just 18 months, spending only $3 million—a fraction of the traditional costs. Now in phase two clinical trials, this drug demonstrates how AI can revolutionize medical research by drastically reducing development time and expenses, offering hope for patients who previously had none.
Beyond medicine, AI is also enhancing climate science. Researchers use machine learning models to analyze large datasets, improving weather predictions and assessing environmental changes. For example, AI helps NASA process satellite images to track deforestation and climate shifts in real time, leading to more informed policy decisions. AI-driven robotic scientists are another breakthrough in research. In chemistry labs, AI-powered robots conduct experiments, reducing human error and increasing efficiency. A single robot scientist in a University of Liverpool lab completed 700 experiments in eight days, a feat that would take a human PhD student four years to accomplish. This advancement enables scientists to focus on higher-level problem-solving while automation handles repetitive tasks.
Despite its benefits, AI in science comes with ethical challenges. The rise of AI-generated fraudulent research has raised concerns about data integrity, as some researchers have unintentionally published AI-generated errors. Additionally, human biases in AI models can impact results, emphasizing the need for transparency and rigorous validation in scientific research.
AI’s potential in science is vast. Whether it’s finding new drug molecules, enhancing climate models, or automating laboratory experiments, AI is driving a golden age of scientific discovery. While challenges remain, overcoming regulatory and ethical hurdles will allow AI to transform science for the better, unlocking solutions to some of humanity’s most pressing problems.
Feb 25, 2025
Along with other industries, the field of medicinal chemistry has also taken an interest in the application of artificial intelligence (AI). AI drug design (AIDD) offers enhanced capabilities property prediction and molecular generation. Compared to traditional methods, AIDD is a lot quicker in its ability to process vast amounts of data to make accurate predictions, it also allows for cost reduction in drug development. Computer aided drug design (CADD) has been applied to make drug design more efficient by making predictions about the relationship between a molecule's activity and its structure. It features some challenges as molecular docking and quantitative structure-activity relationships (QSAR) often face challenges related to accuracy and reliability, as they can produce false positives or negatives due to the simplifications and assumptions inherent in their models. These challenges highlight the need for more advanced and flexible approaches, such as Artificial Intelligence Drug Design (AIDD), to overcome the limitations of traditional CADD methods. Some key points to address with AI in pharmacy are policy implications. Regulatory agencies face challenges in integrating AI while ensuring reliability and safety in clinical trials approvals, as well as post market surveillance. The quality and availability of data, as AI models require large, high-quality datasets to make accurate predictions, and access to such data can be restricted due to privacy concerns and regulatory constraints. Integrating AI with traditional methods and existing workflows also requires significant changes in infrastructure and processes, which can be resource-intensive. Lastly, the high computational demand of AI models and the need for scalability present technical challenges that must be addressed to fully leverage AI's capabilities in drug safety assessments. AI integrates diverse data types, enabling comprehensive insights into drug mechanisms and potential side effects, and supports high-throughput virtual screening of large chemical libraries. Overall, AIDD represents a transformative advancement in drug design, offering enhanced capabilities, efficiency, and innovation.
Feb 25, 2025
Let’s be real, AI is totally helping students get work done. It’s like having a personal assistant that helps with essays, math homework, and gives you the gist of a whole book in seconds. But here’s the thing: is it making students think less? Some people are worried that because of AI, especially Generative AI, is doing so much of the heavy lifting, students aren’t getting the same mental challenge they used to. The skills we all need, like thinking critically, solving problems, and being creative, are getting outsourced to computers. There used to be a time where we had to memorize phone numbers, now we just hit a button and bam, it’s done. That’s similar to what’s happening with school. If students aren’t really diving into the material, their brains aren’t getting the exercise they need to get stronger. It’s all about the journey, not just the destination. Since AI is like a fast-food drive-thru for answers, students don’t have to sit with a problem for ages anymore. They get the info and zoom on to the next thing. This means they’re getting worse at focusing for a long time, which is a big factor when required to think critically and build their knowledge. However, even with all these drawbacks it's important to acknowledge that AI can be super helpful... if you use it the right way. It can help with generating ideas, be like a personal tutor, and even save you some time to focus on the really important stuff. The problem is when students start using it to do all their thinking for them. So, what do we do? Educators need to adapt with the times. Instead of banning AI like it’s some kind of cheat code, they should show students how to use it without letting it take over their brains. Schoolwork should be about the why and how, not just the what. That way, students are forced to develop their thinking and reasoning skills. AI isn’t going anywhere, so we’ve got to figure out how to live with it. Will students use it to be smarter, or will they just let it do all the work? That’s the real question.
Feb 25, 2025